Oligonucleotide (DNA & RNA) Customized Service - Solid Phase Synthesis
Oligonucleotide (DNA & RNA) Customized Service - Solid Phase Synthesis
Oligonucleotide is known as a class of short-chain nucleotides containing about 20 nucleosides (including deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA). Oligonucleotides can pair to its complementary chain easily according to the base pairing principle. It represents a unique mechanism of action for disease treatment and is a hot spot in the field of medicinal development in the past decade. Oligonucleotides include antisense oligonucleotides, immunostimulatory oligonucleotides, ribozymes, mircoRNAs, siRNAs, nucleic acid aptamers, and mirror oligonucleotides, and so on. Ganbaoli can provide custom synthesis for oligonucleotides, including conventional and structurally modified siRNA oligonucleotides. The synthetic scale, ranging from micrograms to hundred grams, can help meet the needs of scientific research and drug R&D. The synthesis process is stable, high yielding, good repeatability with complete means of quality control and product of high purity.
Features:
Synthesis and QC | Fully automatic solid phase synthesizer by solid-phase phosphoramidite method, GMP-compliant synthetic workshop ensures the cleanliness level of the final product. |
Synthetic scale | μg~g |
Nucleosides | RNA (A, C, G and U) |
Modifications | 2'-O-methyl (OMe)、2'-fluoro (F)、Phosphorothioate、Amino C6 linker、Cholesterol and other cus-tom orders. |
Purification | HPLC |
Delivery cycle | Usually 20 working days. The actual lead time depends on the sequence and quality requirements. |
Appearane | Lyophilized powder |
The basic steps of solid phase oligonucleotide synthesis - solid-phase phosphoramidite method:
1)DMT deprotection: removal of the DMT protecting group on the 5'-OH group of the first neucleoside attached to solid phase;
2)Coupling: coupling of a second base in the 3'→5' direction;
3)Capping: remaining unreacted 5'-OH of the first base is capped, so that it will not participate in subsequent reaction;
4)Oxidation: oxidation of the resulting nucleoside phosphite to a more stable nucleoside phosphate (ie, oxidation of trivalent phosphorus to pentavalent phosphorus);
5)The above steps are repeated until the desired sequence is completed;
6)Aminolysis and cleavage: Upon completion, the synthesized oligonucleotide is cleaved from the solid phase and protecting groups are deprotected by aminolysis (CPG);
7)TBDMS Deprotection: removal of the TBDMS group of the 2'-glycosyl;
8)Purification: HPLC separation and purification;
9)Filtration and sterilization;
10)Lyophilization.
Solid phase synthesis diagram: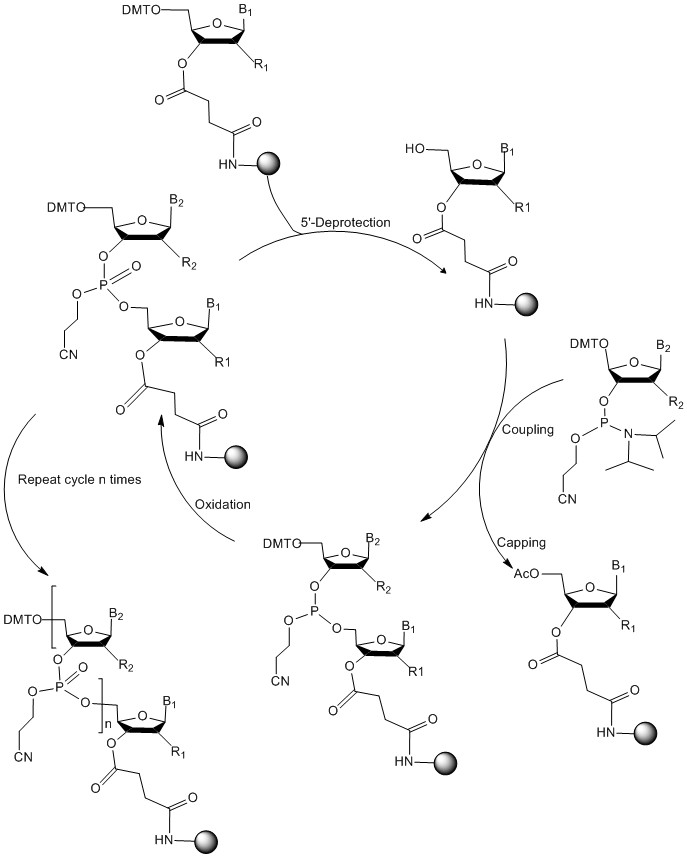
Note: n: 10~30;
B1, B2:Uracil U, Cytosine C, Guanine G, Adenine A, Thymine T;
R1, R2:OTBDMS or H or OMe.



